India’s Unincorporated Non-Agricultural Sector: A Key Driver of Inclusive Growth and Employment
India’s Unincorporated Non-Agricultural Sector: A Key Driver of Inclusive Growth and Employment
Published on :- February 14th, 2025
SDG 8, one of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), focuses on promoting sustained economic growth, productive employment, and decent work for all. It aims to create job opportunities regardless of individuals' backgrounds, gender, or disabilities, while also improving living standards, reducing market inequalities, and encouraging entrepreneurship and innovation.
Enterprises in the unincorporated non-agricultural sector play a pivotal role in contributing to the country's GDP and creating employment opportunities. This sector forms a critical component of the supply chain and significantly impacts economic growth.
To better understand the economic and operational dynamics of this sector, the Annual Survey of Unincorporated Sector Enterprises (ASUSE) was initiated by the NSSO and released its first report in 2024. The survey exclusively measures the characteristics of unincorporated non-agricultural establishments in manufacturing, trade, and other services. In this Data Dialogue, we explore the details of this survey and highlight some key data insights from the ASUSE.
As of 2023-24, an estimated 7.3 crore establishments operate within this sector, with more than half (54%) located in rural areas. These establishments collectively employ 12.06 crore workers, of which 53.5% are from urban areas.
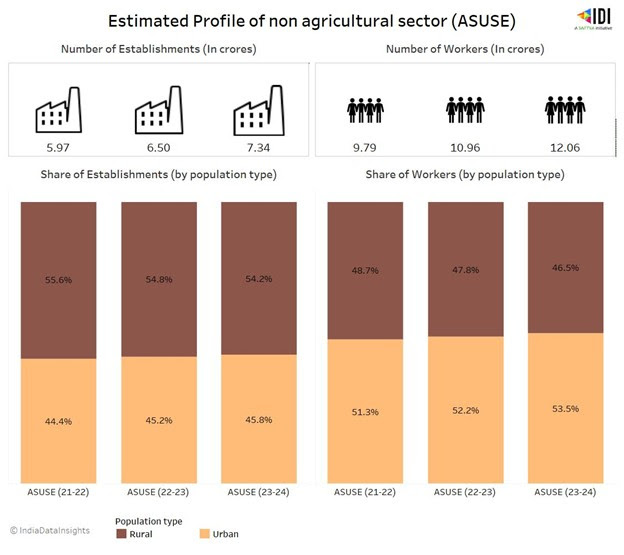
Comparing the ASUSE surveys, the number of establishments increased by ~23% since 2021, and the workforce also grew by 23.2%, highlighting the sector’s continued expansion and its critical role in supporting both rural and urban employment. The establishment of urban establishments and the employment of the urban population in the informal sector have been steadily increasing.
Note: Three surveys were conducted, ASUSE (21-22) with timeframes as Apr 21-Mar 22 and ASUSE (22-23) with timeframes Oct 22-Sep 23.
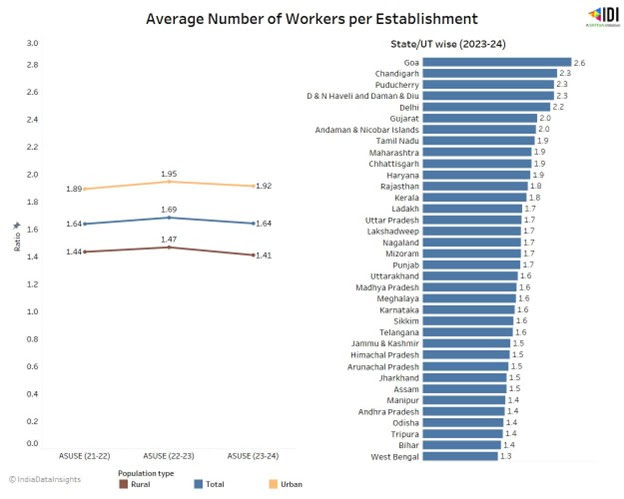
As of 2023-24, there are over 397 lakh rural establishments employing 561 lakh workers - averaging 1.4 workers per establishment. However, the number is about two workers per urban establishment. Interestingly, all Union Territories (except Jammu & Kashmir) have an average of more than two workers per establishment, whereas in larger states, the worker-to-establishment ratio ranges between 1.3 and 1.9.
Of the 7.3 crore establishments in the non-agricultural sector, 1/3rd of the establishments are located in Uttar Pradesh (12.8%), West Bengal (12.6%), and Maharashtra (8.8%) which also employ 1/3rd of the total workers employed in this sector.
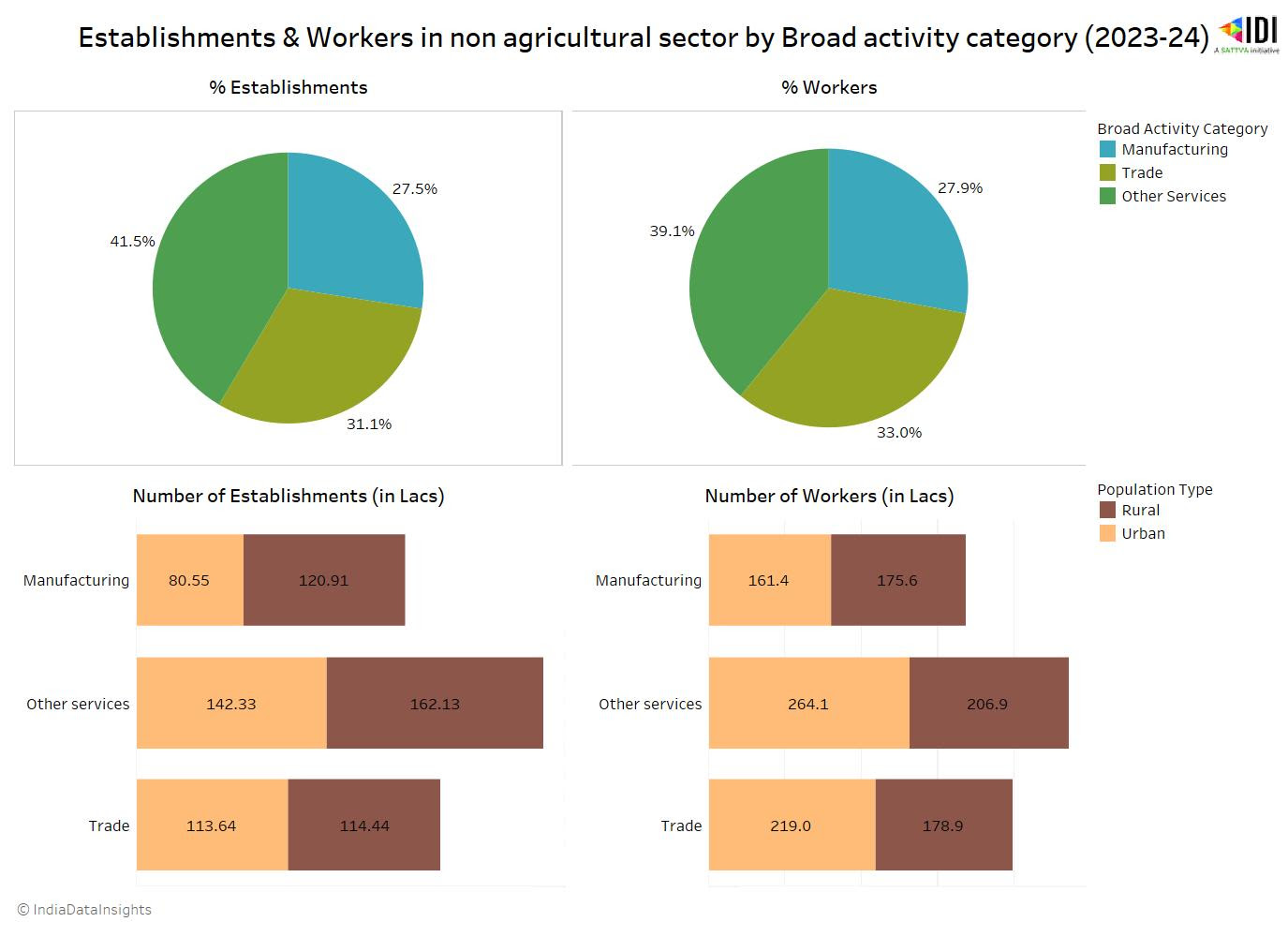
According to the latest ASUSE 2023-24 survey, the service sector emerged as the largest contributor to India's informal sector, accounting for 41.5% of establishments, followed by the trade sector at 31.1%. The service sector alone has established 162 lakh rural establishments, supporting 206 lakh individuals in rural areas.
Notably, over 50% of service establishments are rural and more than 50% of the workforce in the service category is from urban areas. A similar trend was observed in the trade sector, where 60% of manufacturing establishments are situated in rural areas, and 52% of the workforce in manufacturing is from rural areas.
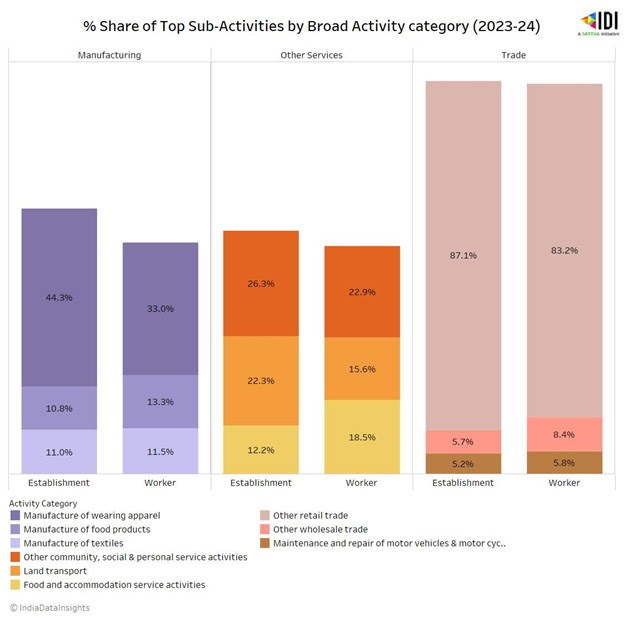
The survey analysed 45 sub-activities under three broad activity categories (Manufacturing, Service, and Trade) and found that Other retail trade (Trade), Manufacture of wearing apparel (Manufacturing), and Other community, social, and personal service (Service) emerged as the top three largest shares of unincorporated non-agricultural sub-activities establishments. These also generated the largest share of employment in 2023-24.
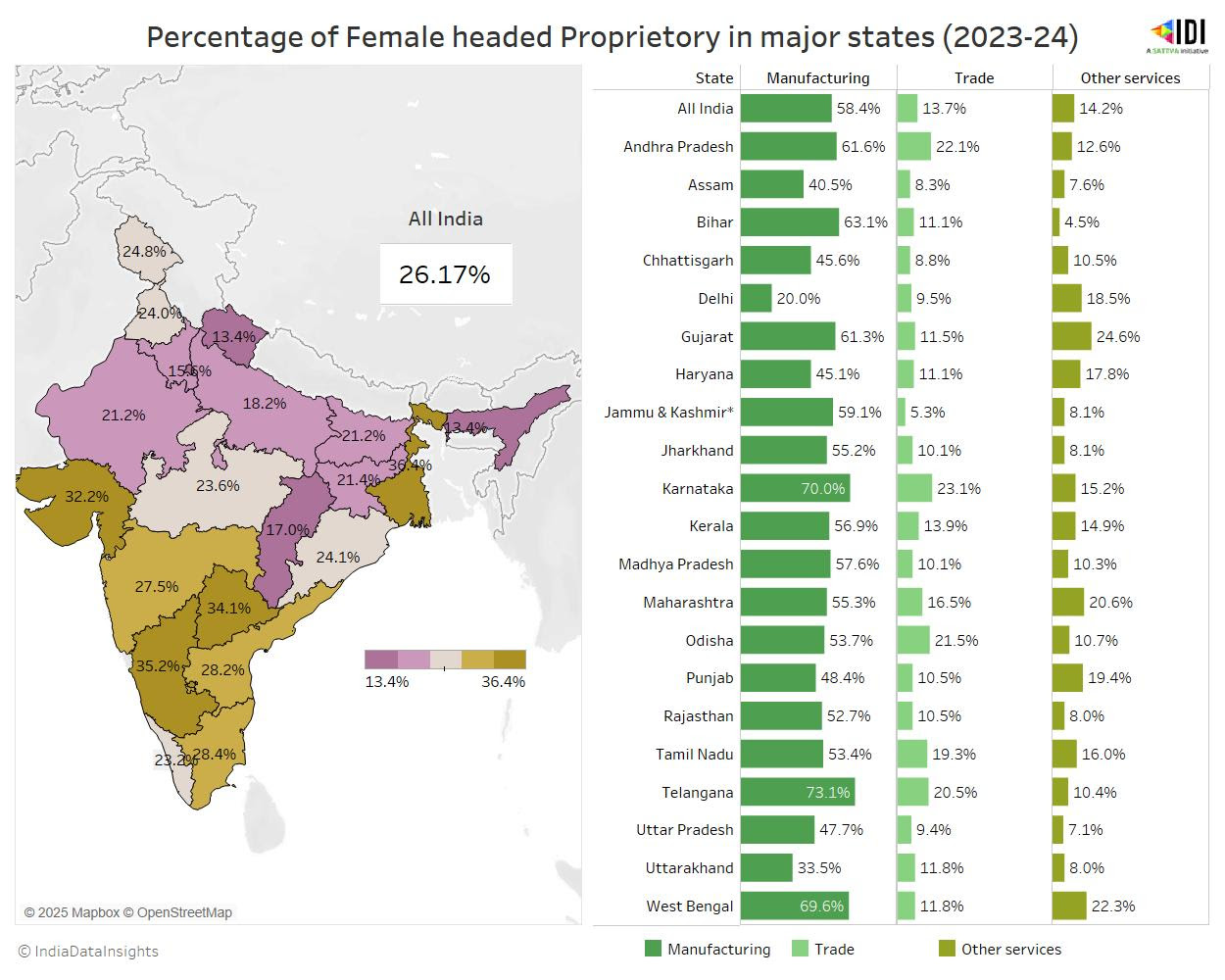
Another important parameter for establishments in the unincorporated sector is the “Ownership” which is categorised as Proprietary, Partnerships, and Self-Help Groups (SHGs), Societies/Trusts, Cooperatives, and other categories. According to ASUSE 2023-24, establishments with proprietary ownership are dominant – accounting for about 95% of establishments across both rural and urban areas.
At the all-India level, one in every four proprietary establishments is owned by a woman. Among the states, female proprietors lead about one-third of proprietary establishments, particularly in West Bengal (36.4%), Karnataka (35.2%), Telangana (34.1%), and Gujarat (32.2%).
Women also play a significant role in the unincorporated manufacturing sector, where they constitute over 50% of proprietors across all 21 major states. Notably, nearly three-fourths of manufacturing establishments in Telangana and two-thirds in Karnataka and West Bengal are led by women.
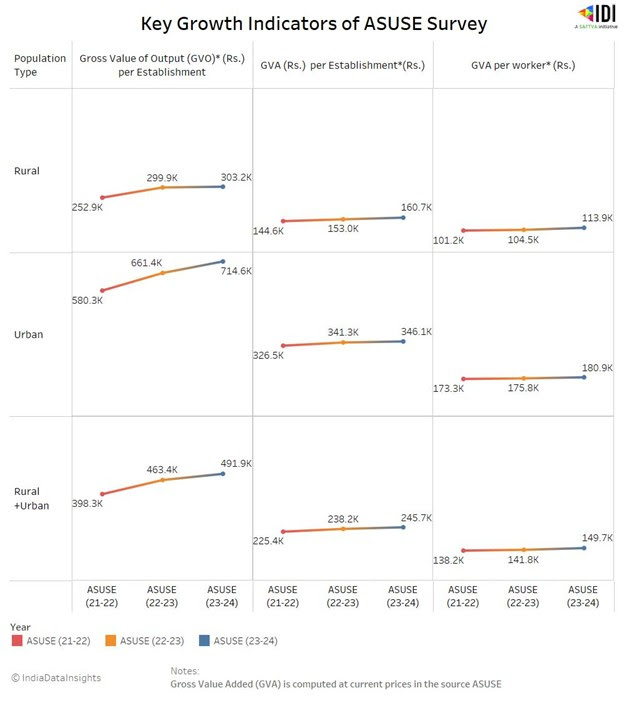
While the overall share of establishments belonging to the informal sector is higher in rural areas, the Gross Value Added (GVA) and Gross Value Output per worker (GVO)—a measure of labour productivity—are significantly higher in urban areas, which shows greater economic activity and productivity in urban establishments. The GVA per establishment in urban areas is double that of rural areas. This indicates better income opportunities for informal labor across urban sectors.
Between 2021-22 and 2023-24, the overall GVA from the unincorporated sector increased from 13,40,046 crores to 17,97,278 crores, marking a 34% increase. A majority of the contribution in GVA in this sector is by the other service broad activity.
The unincorporated non-agricultural sector is a vital driver of economic growth, job creation, and inclusivity in India. The sector's expanding footprint, rising participation of women entrepreneurs, and increasing share in contributing to India's GVA are fostering inclusive development aligned with the goals of SDG 8.
As India continues to promote entrepreneurship, innovation, and sustainable economic practices, the unincorporated sector will remain a critical focus area for strengthening livelihoods and reducing inequalities across both rural and urban communities.
For more data insights on SDG 8, click here.
