This month from India Data Insights we are looking at SDG 7…
This month from India Data Insights we are looking at SDG 7…
Published on :- January 9th, 2023
The National Energy Conservation Day is celebrated every year on 14th December 2022. The day has been an option to showcase the achievements of the nation in energy efficiency and conservation. As per UN Sustainable Development Report 2022, India ranked 88th in the world for energy availability and access, and the country has shown promising signs as it is moderately improving.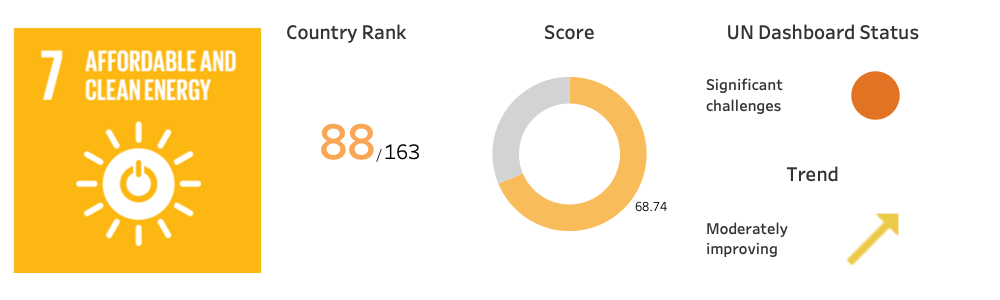
The National Energy Conservation Day is celebrated every year on 14th December 2022. The day has been an option to showcase the achievements of the nation in energy efficiency and conservation. As per UN Sustainable Development Report 2022, India ranked 88th in the world for energy availability and access, and the country has shown promising signs as it is moderately improving.
- By 2030, ensure universal access to affordable, reliable and modern energy services
- By 2030, increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix
- By 2030, double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency
- By 2030, enhance international cooperation to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology, including renewable energy, energy efficiency and advanced and cleaner fossil-fuel technology, and promote investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology
- By 2030, expand infrastructure and upgrade technology for supplying modern and sustainable energy services for all in developing countries, in particular least developed countries, small island developing States, and land-locked developing countries, in accordance with their respective programmes of support.
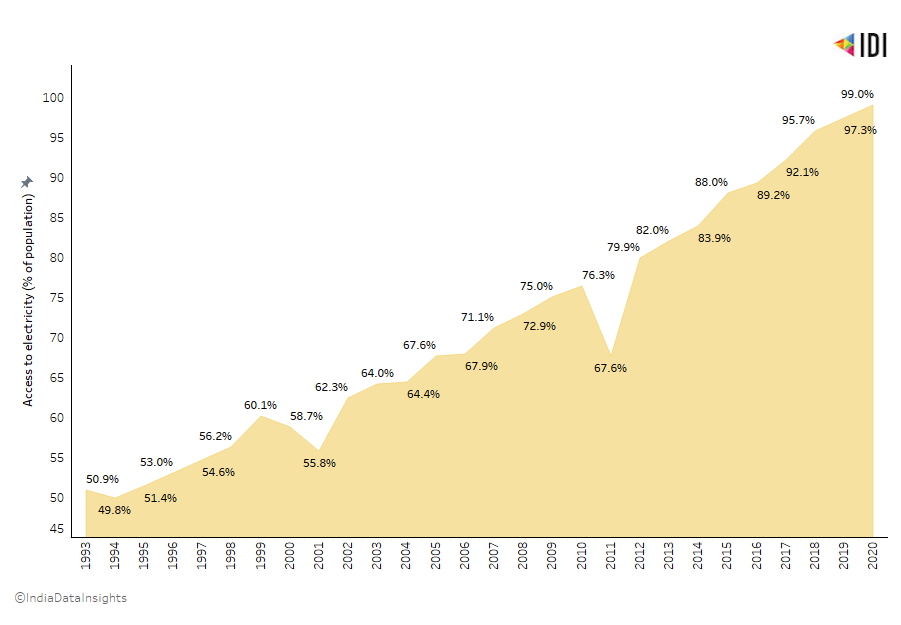
In the last three decades, India has seen a consistent growth in the percentage of population having access to electricity.
In 1993, ~50% of India’s population had access to electricity. However as of 2020, more than 99% of the population now has access to electricity!
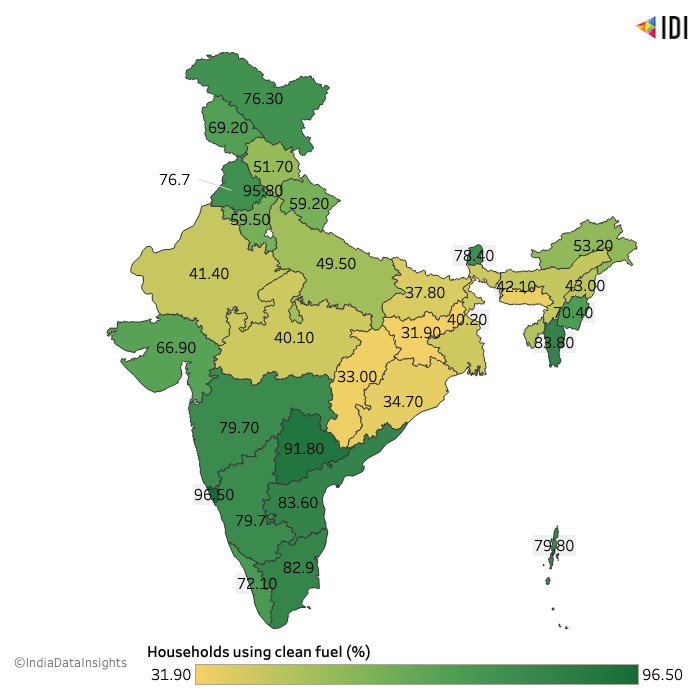
While there has been an increase in the availability of electricity, clean cooking fuel is still used across the nation. A 2019-2021 National Family Health Survey (NFHS 5) shows that 58.6% of Indian Households used clean cooking fuels - 89.7% of Urban and 43.2% of Rural. The usage is predominantly seen in Goa, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Mizoram. Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Bihar and West Bengal show the lowest utilisation of Clean Cooking Fuel.
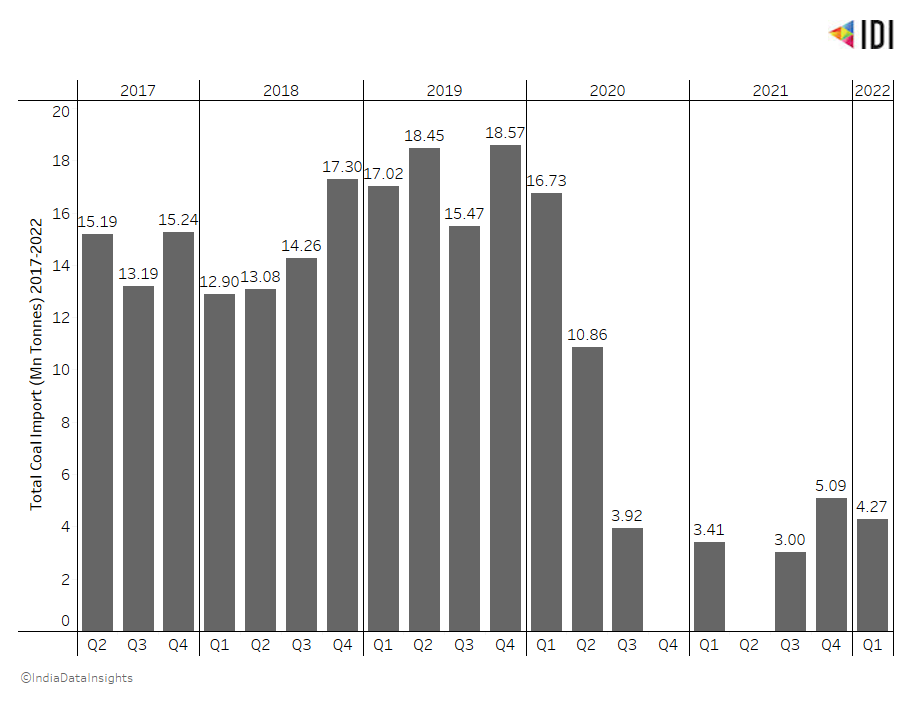
Coal has remained one of the country's most significant contributors to electricity generation. In India, coal imports were the highest during the last quarter of 2019, with 18.57 Million Tonnes of coal being imported. Approximately 12000 Million Tonnes of more coal was imported in 2019 compared to 2018.
The impact of COVID-19 is also seen in the amount of coal imported into the country, especially during the nationwide lockdown in 2020.
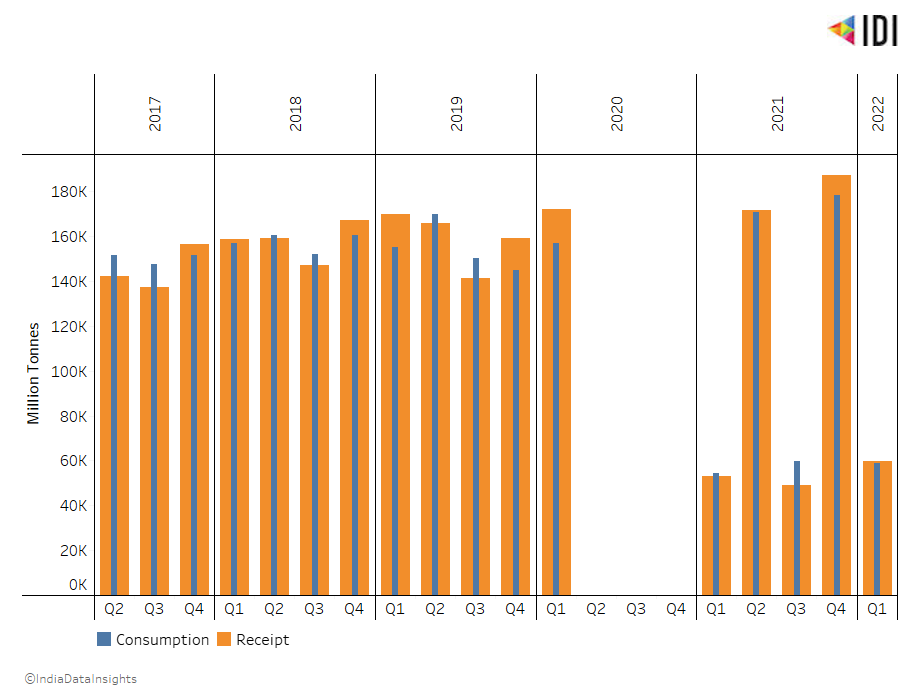
Similarly, data on coal consumption is unavailable or found to be lower during the COVID-19 period, especially during the nationwide lockdown in 2020. Despite the impacts of COVID-19, coal consumption grew in the 2nd and 4th quarters of 2021. In Q4 of 2021, coal consumption reached its highest level in recent years.
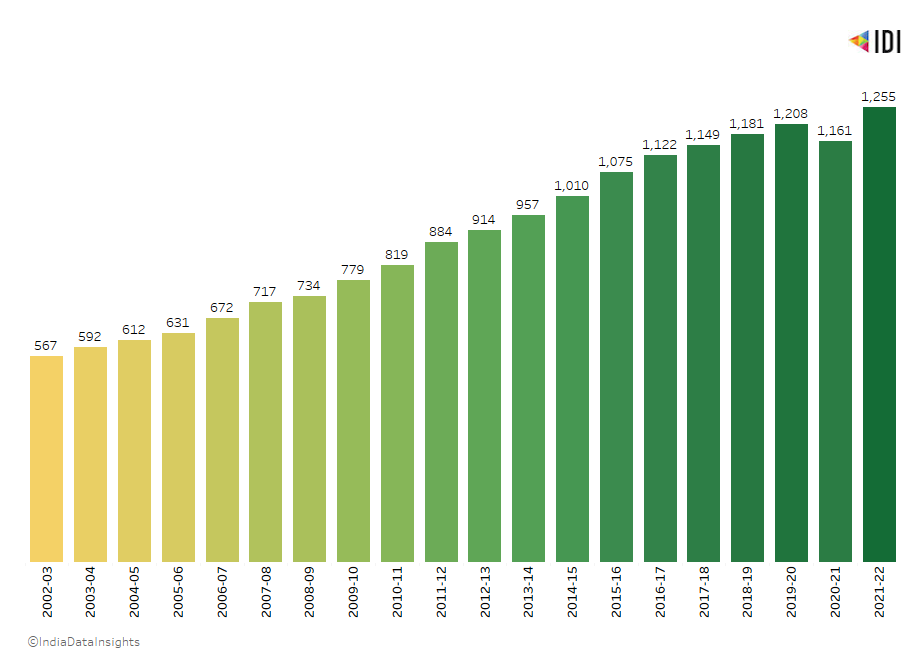
Per capita consumption of electricity has more than doubled in the last two decades. In 2002-03 per capita consumption of electricity was 566 kWh. It has increased to 1255 kWh in 2021-22 - a ~120% increase.
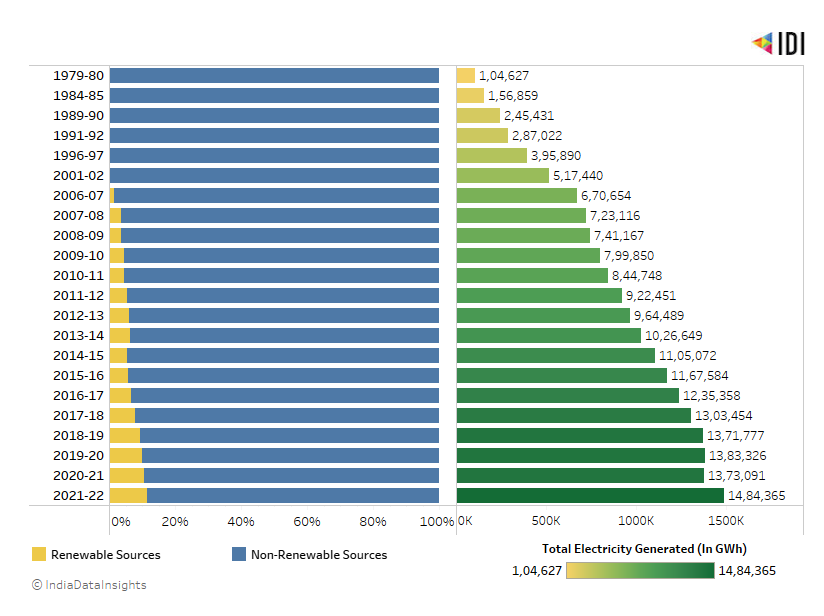
A positive sign is the increasing share of renewables in electricity generation. In 2021-22, India generated 14,84,365 GWh of electricity. Share of energy generated for electricity from renewable resources increased from 1% in 2006 to 10% in 2021-22.
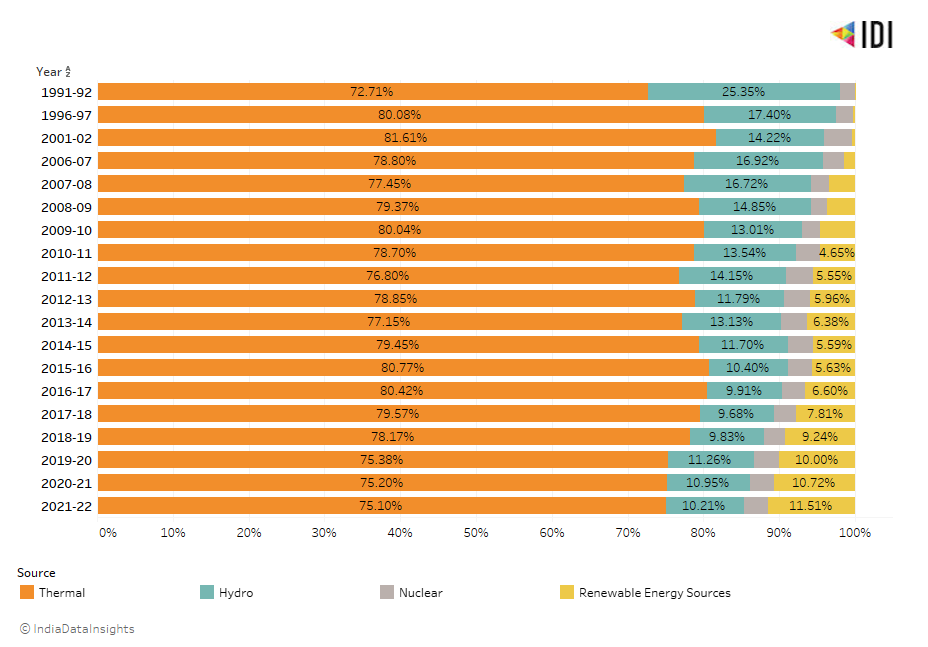
Within non-renewables, energy generation from the Thermal Source (Coal, Diesel, Natural Gas) has increased from ~72% to 75% in the last three decades. Share from Hydro source has however decreased from the year 1991 to 2022 by 15%. And Nuclear energy generation has remained constant at ~3%.
Renewable Energy Source (Small Hydro, Solar, Wind, Biomass Bagasse, Renewables) contribution has increased from 1% to 11.5% from the last two decades 2001 to 2021.
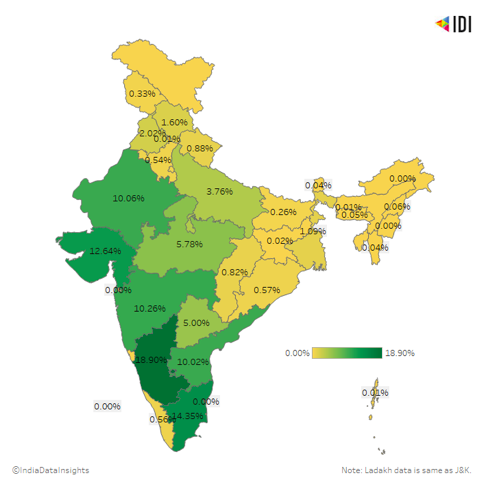
Renewable energy in India is growing in importance across many states, with 10% of the country's electricity production coming from renewable sources. A hopeful sign for the country's future.
As of 2020, 66% of India’s renewable energy comes from 5 states - Karnataka (18.9%), Tamil Nadu (14.35%), Gujarat (12.64%), Maharashtra (10.26%) and Rajasthan (10.06%).
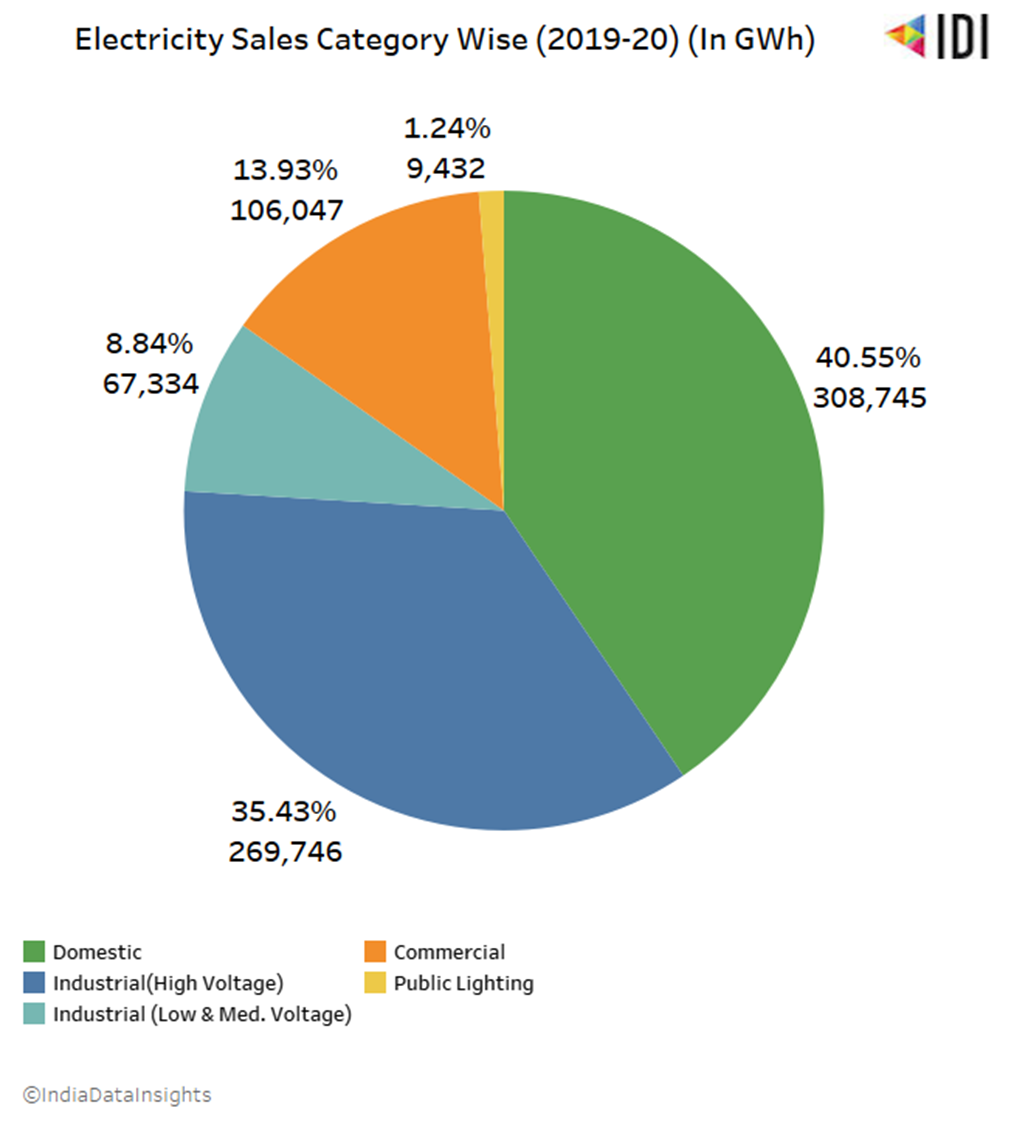
Electricity Sales
The major energy produced in the country is sold for Domestic purposes (40%), followed by Industrial (High Voltage) (35.43%) and Commercial (13.93%) in 2019-20.
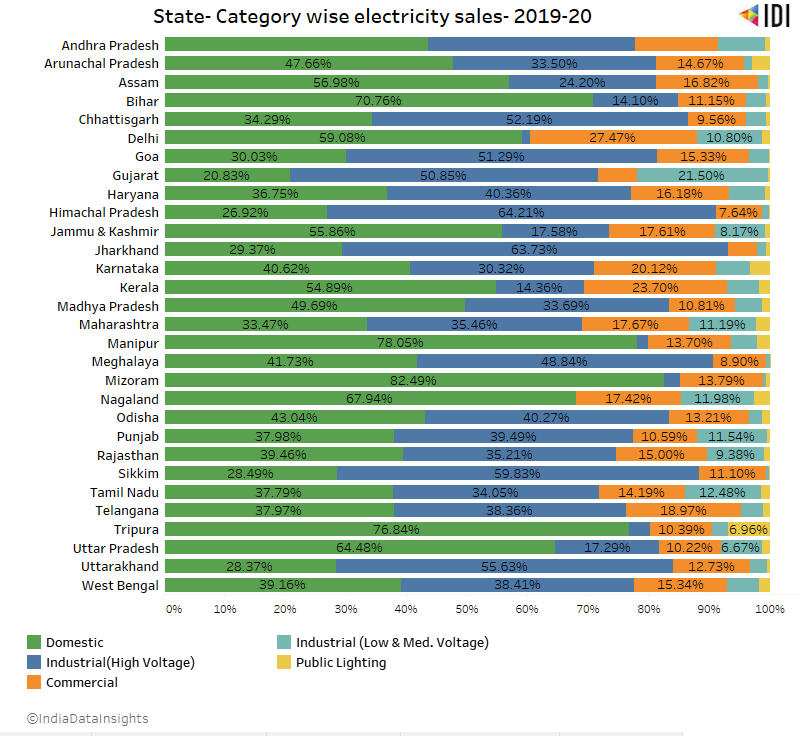
The trend is similar among states as well where states like Mizoram (82.49%), Tripura(76%), Manipur (78%) sell most of their energy produced for domestic purposes. Whereas Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim, and Uttarakhand sell 50% of energy to Industrial Usage.
Through the combined efforts to increase renewables and enable larger access to electricity and clean cooking fuel, India is working towards its goal of providing universal access to affordable, reliable and modern energy services by 2030.
For more assets on SDG 7, click here https://indiadatainsights.com/categories/affordable/
